- Location: Sevilla
- Main Data: 10 MW hot water (+ 5 MW reserve) and 5,000 kg/h steam (+ 2,500 kg/h reserve)
- Technology: High-efficiency steam and water boilers
- Client: Servicio Andaluz de Salud (SAS)
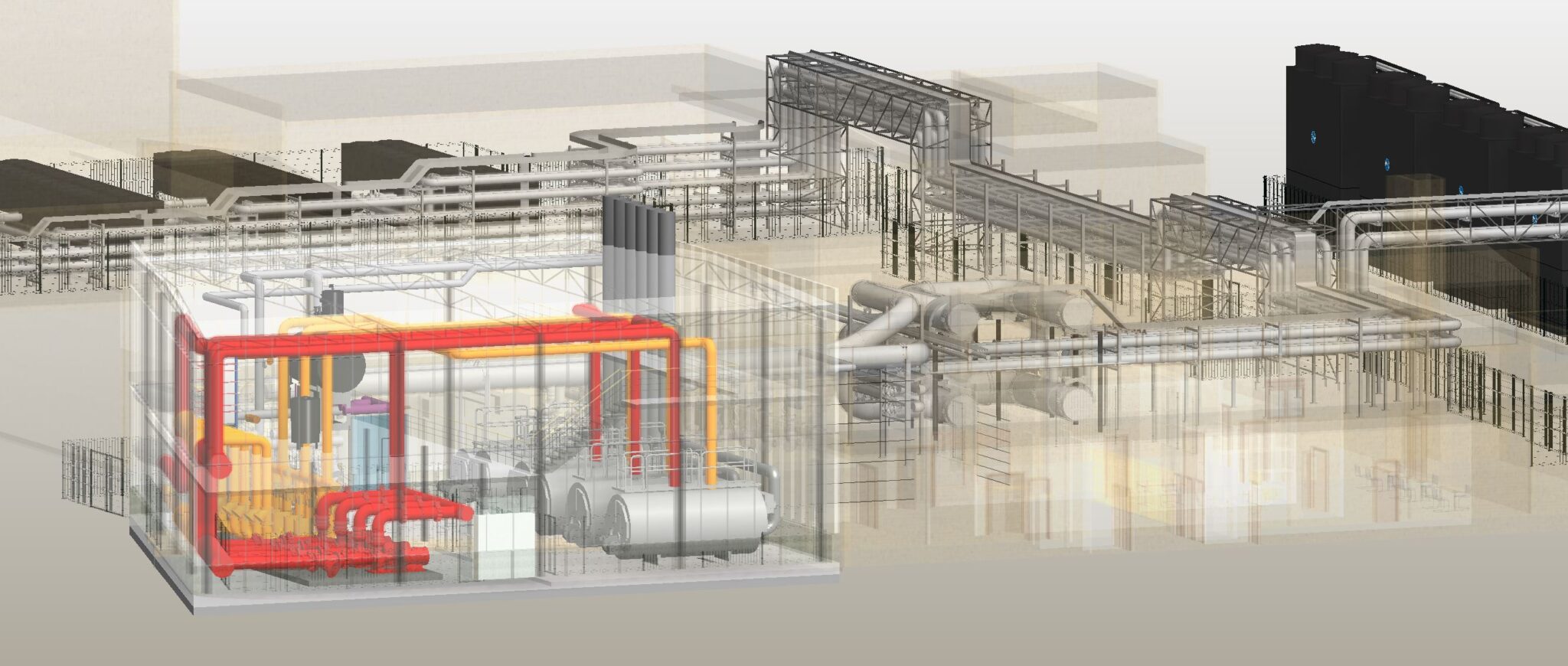
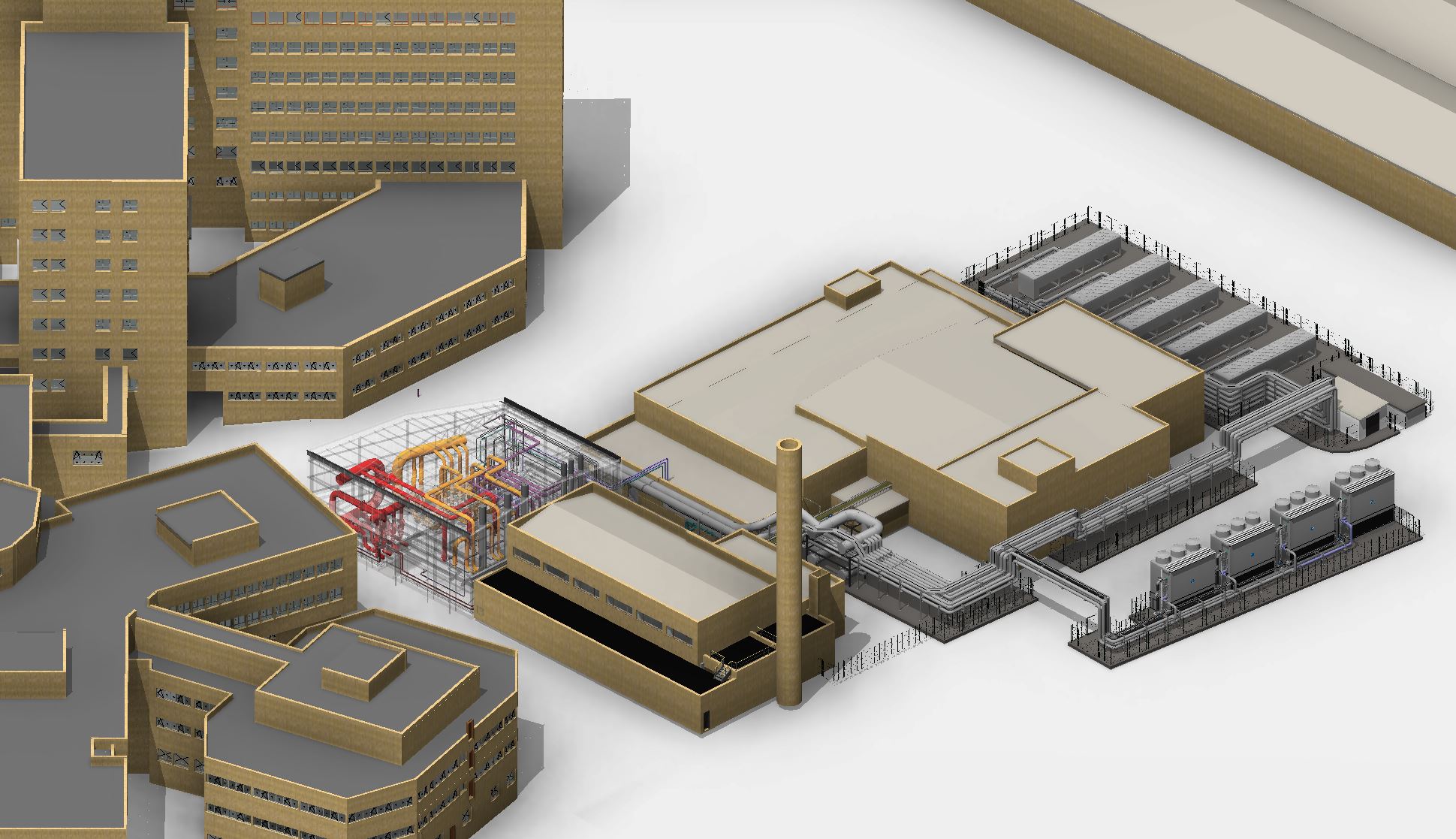
Within the framework of the improvement of the energy efficiency of the Virgen del Rocío hospital complex in Seville, Savener has carried out a complete modernisation of the thermal power plant. This project, developed in collaboration with the Andalusian Health Service, has sought to optimise the hot water and steam production and distribution systems, integrating advanced technologies and innovative energy saving measures to guarantee a more efficient and sustainable operation of the hospital.
The project, 80% financed by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) and 20% by the SAS, has a total initial investment of 7.24 M€.
Scope of the project
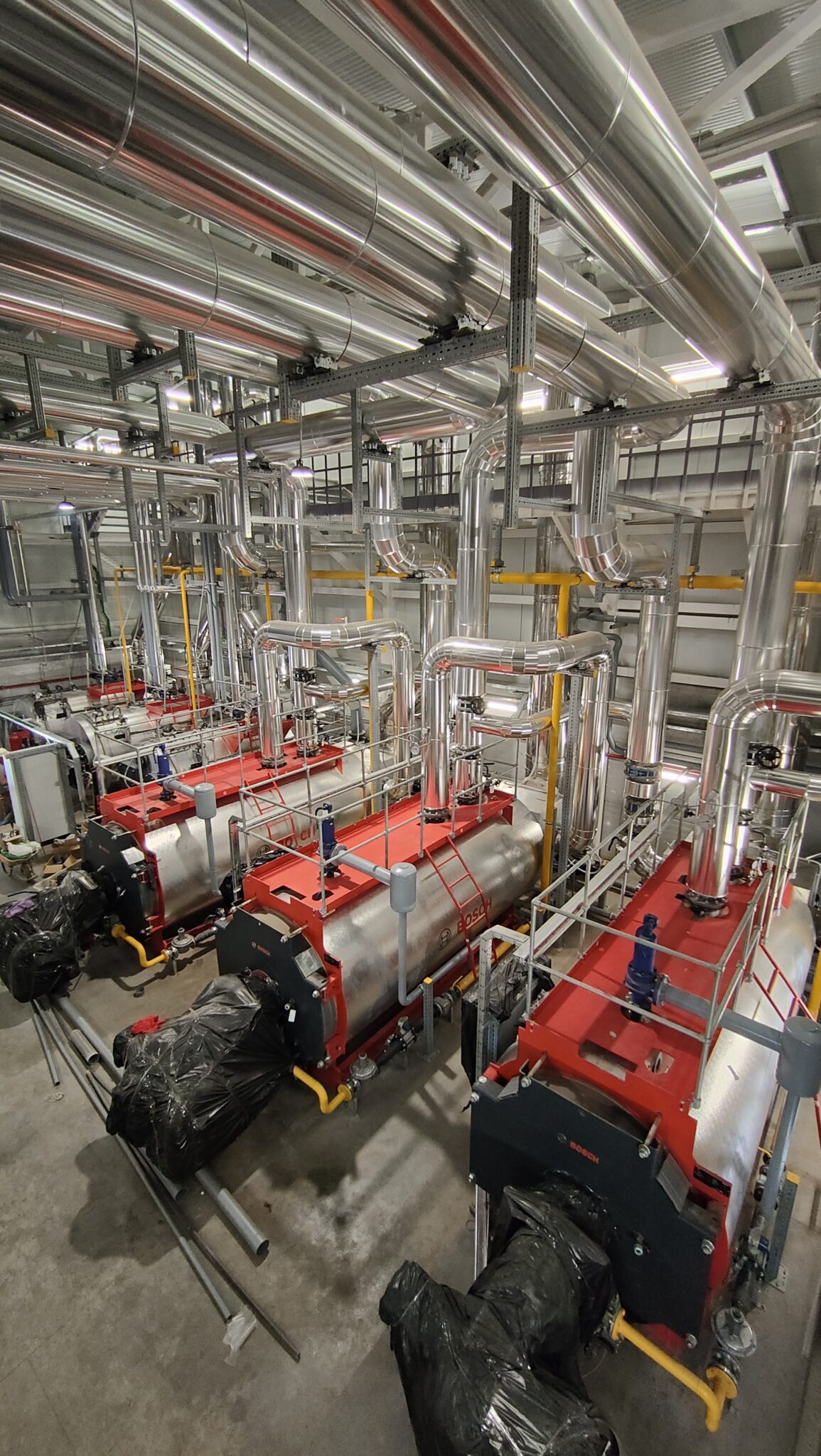
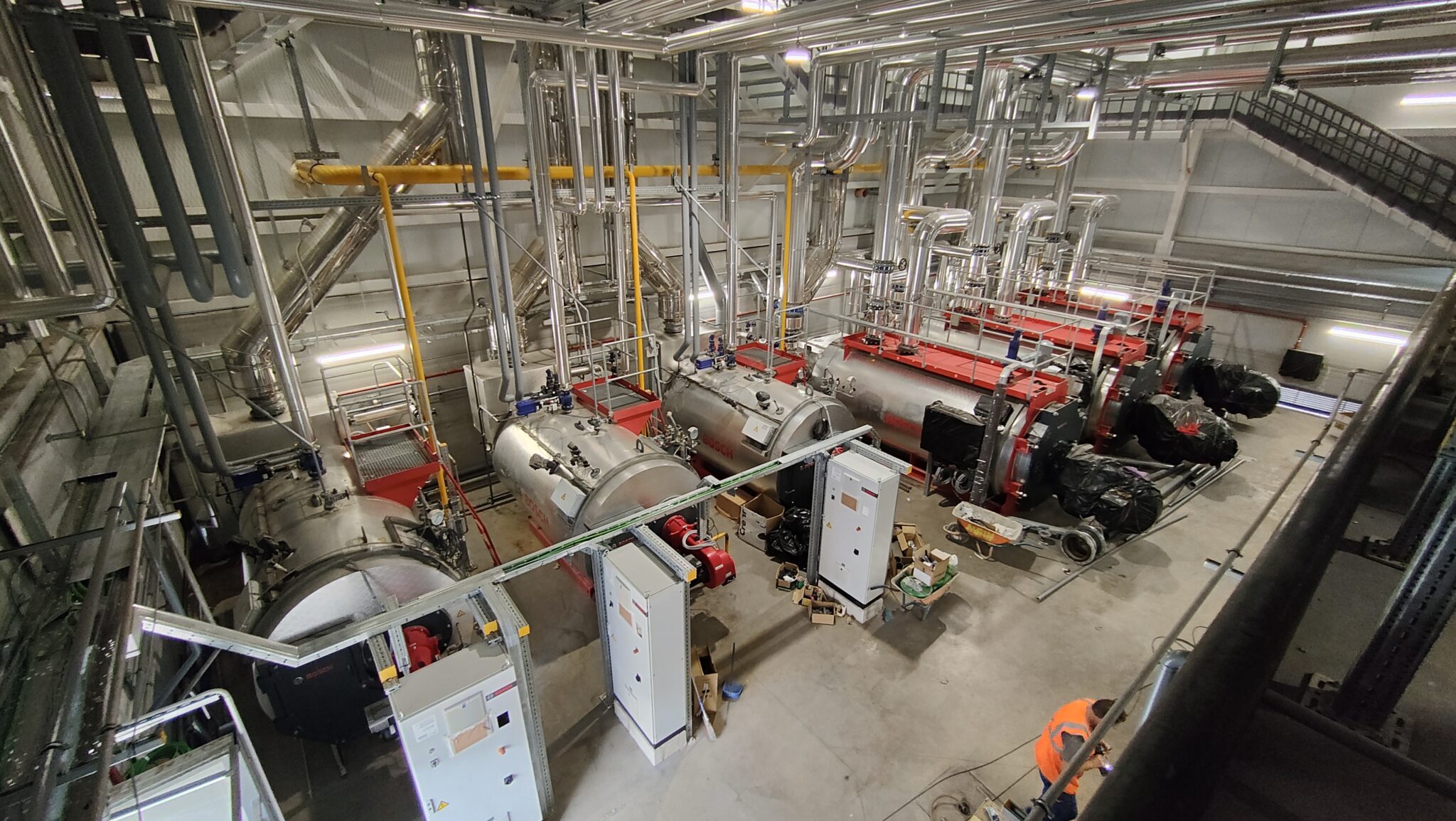
The modernisation of the thermal power plant includes the replacement of the current boilers with high-performance, modulating control equipment, specifically designed to adapt to the hospital’s real demand. These new boilers have a heat recovery system for the combustion fumes, thus increasing energy efficiency and significantly reducing CO2 emissions.
In addition, a condensation heat recovery system has been implemented in the cooling plants of the new refrigeration plant, using this energy to pre-heat water for the production of steam and domestic hot water (DHW) for the hospital. This measure has led to a considerable reduction in energy consumption by harnessing residual energy sources in the hospital’s internal processes.
Technical Details and Benefits
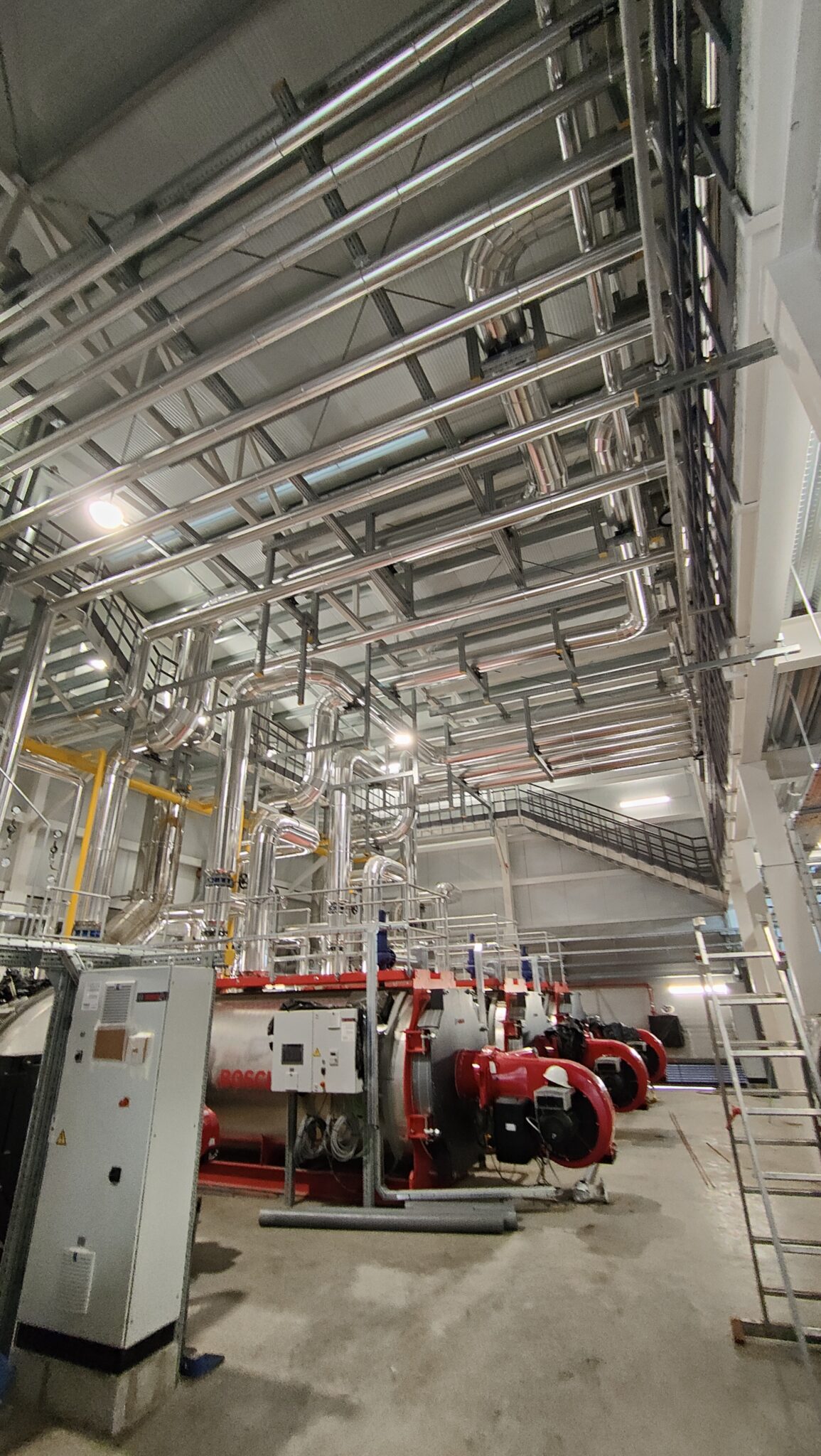
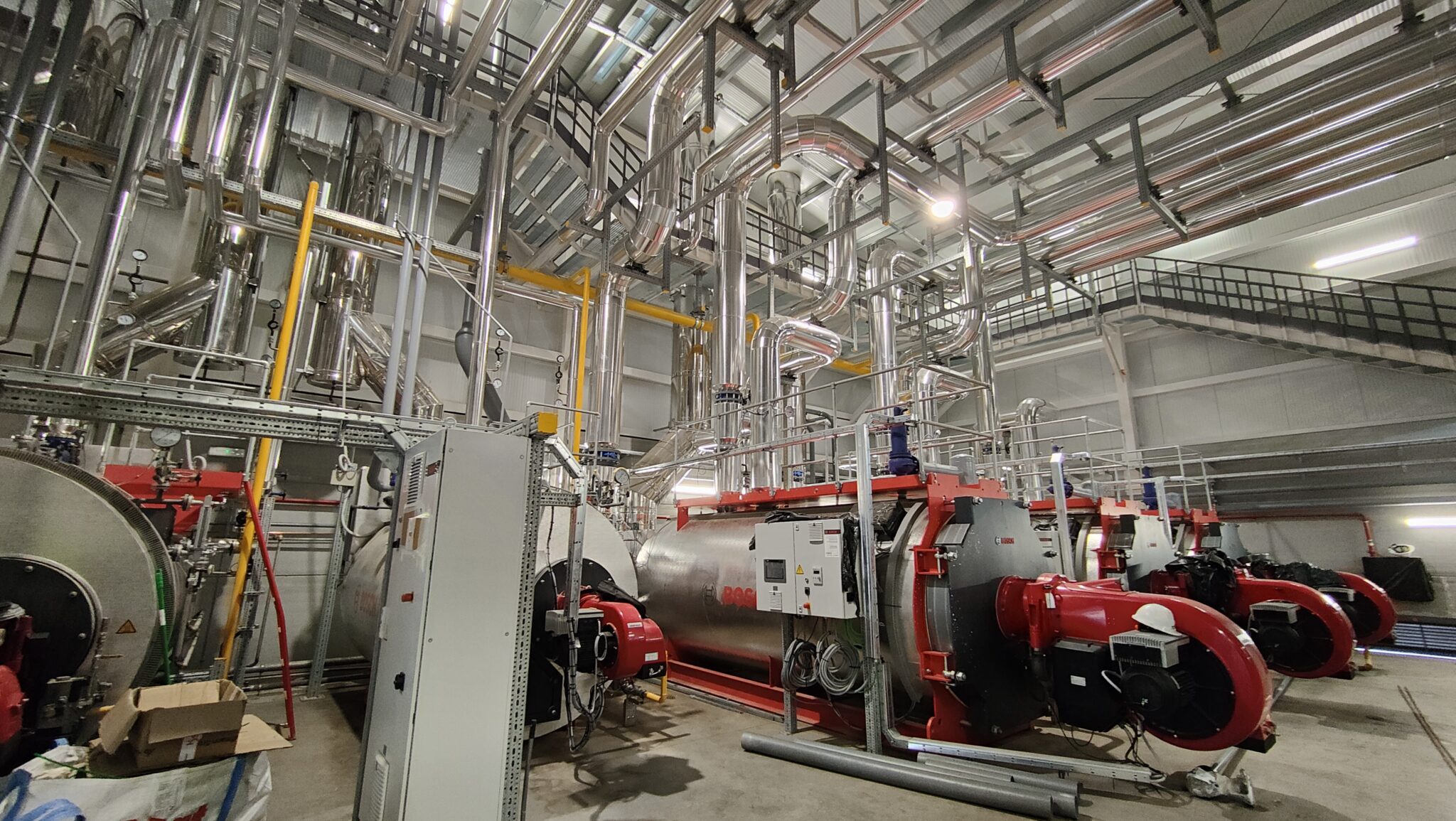
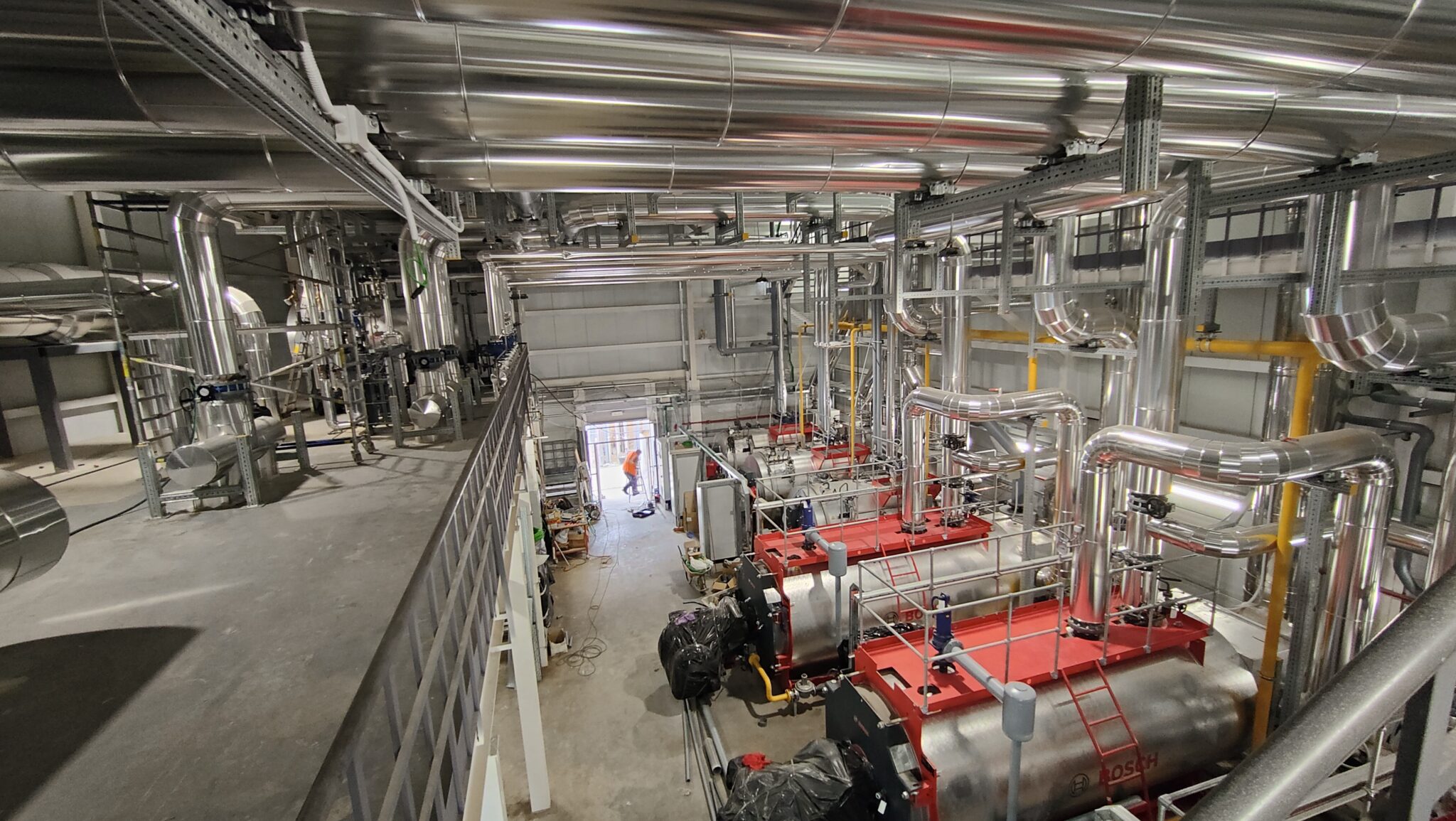
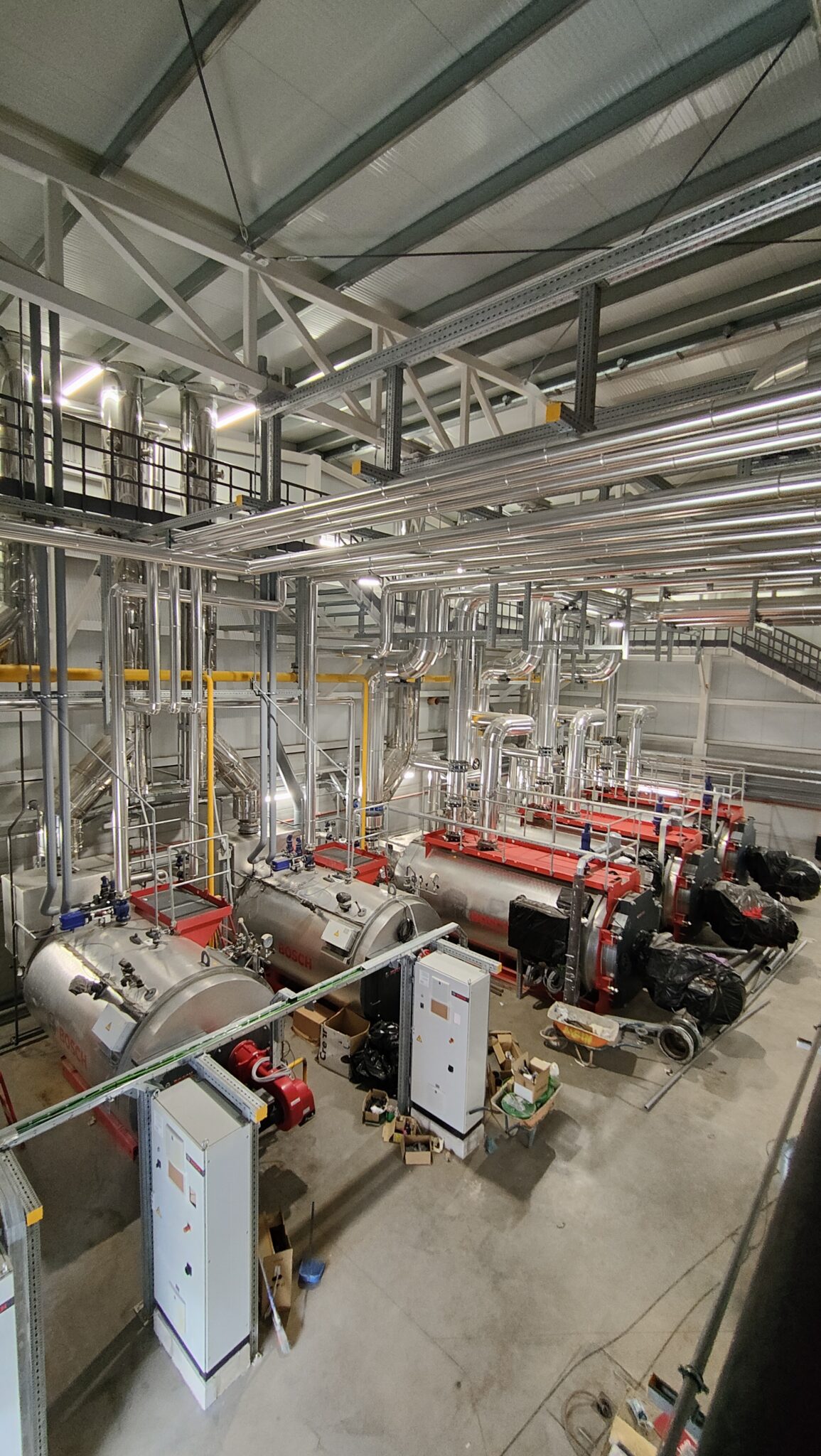
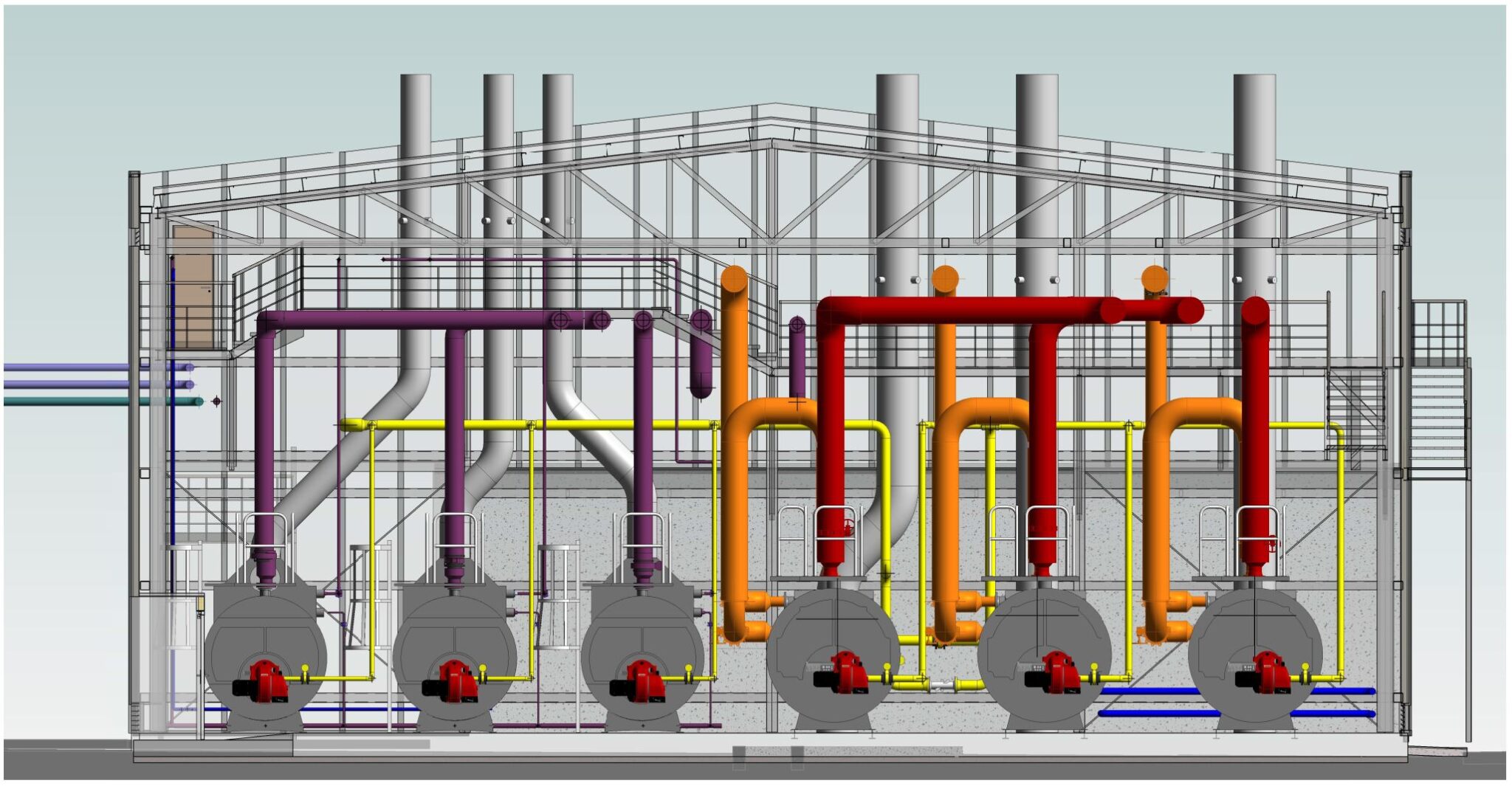
- Hot Water Boilers: The plant is equipped with three high-efficiency shell boilers (with a planned operation of two of them for normal use plus a standby), each with a nominal output of 5,000 kW and the capacity to reach flow temperatures of up to 110°C at a maximum pressure of 6 bar. These horizontally configured, monoblock boilers have an efficiency between 92% and 95.5%, meeting stringent environmental standards for reducing nitrogen oxides (NOx). Their three-flue design allows for greater heat transfer and reduced emissions, while maintaining high durability and low maintenance costs.
- Steam Boilers: The new steam production plant consists of three pyro-tubular boilers with a capacity to generate 2,500 kg/h of steam at 13 bar, normally operating at 11 bar.Two of the three boilers will operate in normal mode, with the third in standby. These boilers incorporate modulating burners with oxygen and speed control systems, as well as a module for heat recovery from the combustion fumes, thus optimising efficiency and reducing energy consumption. They are connected to a degassing tank that heats the make-up water to 102°C, removing dissolved gases for greater efficiency and operational safety.
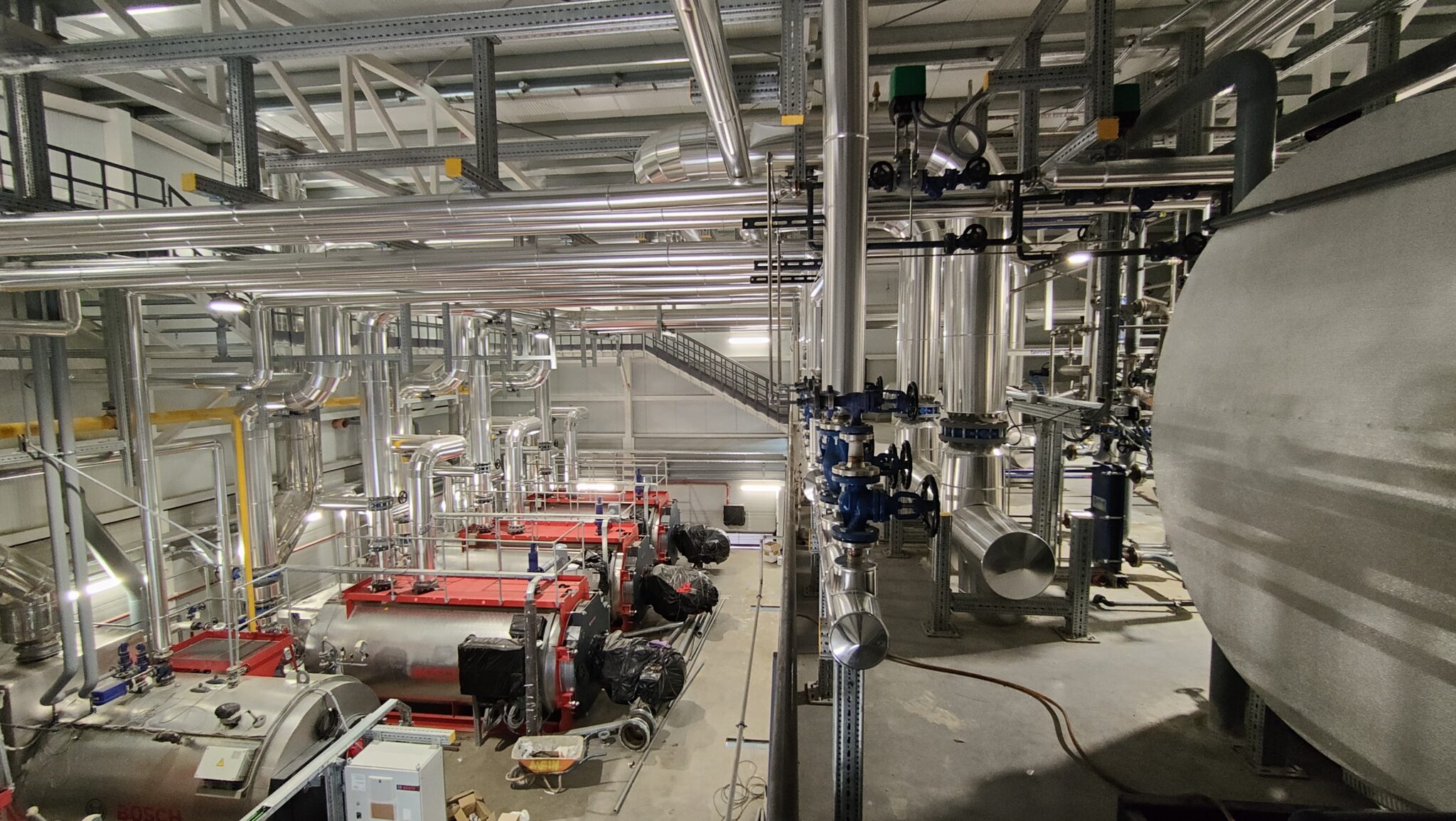
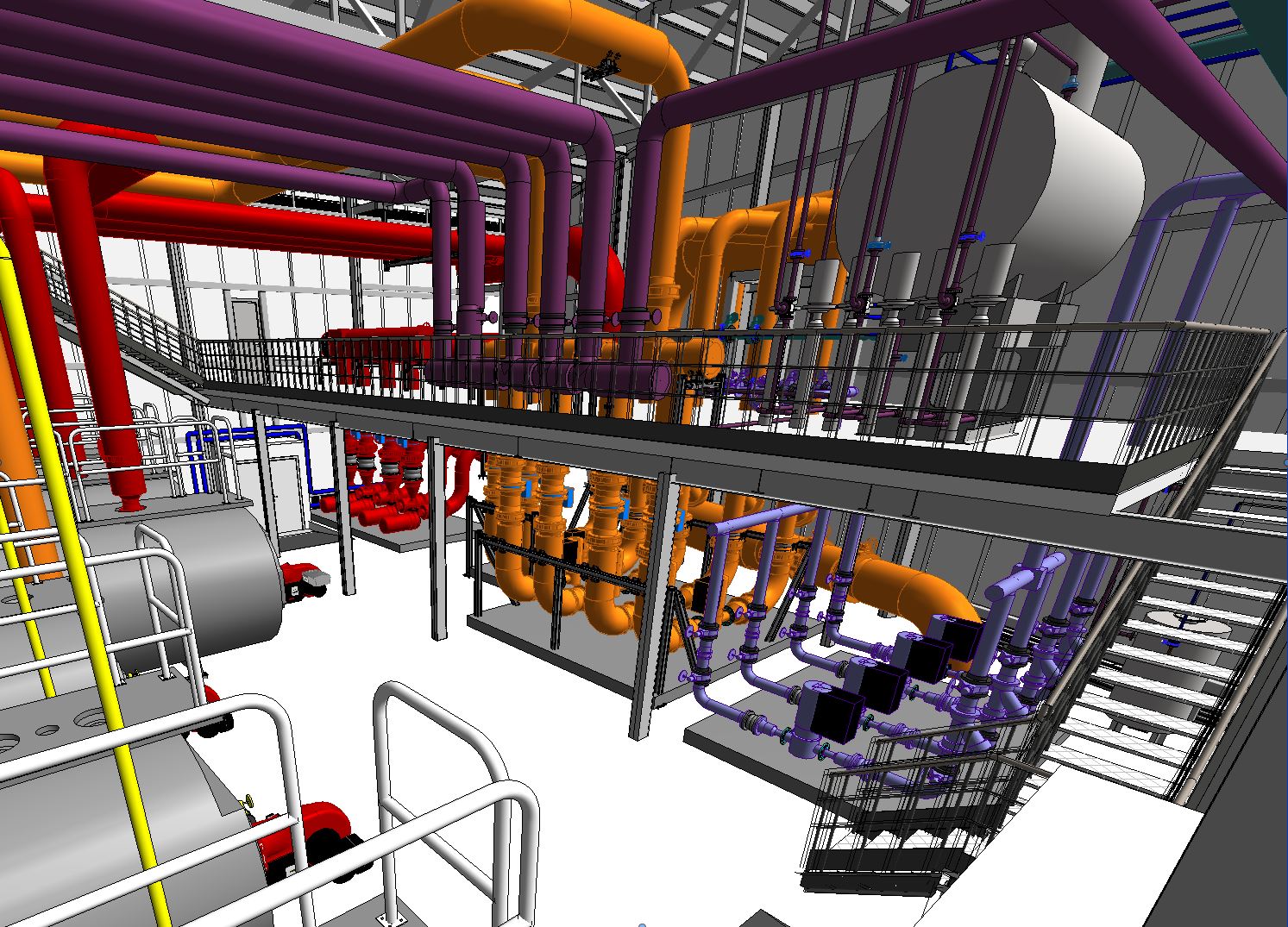
- Reduced Energy Consumption: In addition to the efficiency of the boilers, a system of high efficiency heat exchangers and variable flow pumping units have been installed, which adjust their operation according to demand, maximising energy savings in the heating and DHW circuits.
- Control and Monitoring Technologies:The modernised thermal power plant is fully integrated into the hospital’s SCADA control system, allowing for remote monitoring and continuous optimisation. The installation of speed and oxygen monitoring systems on the burners ensures accurate and efficient operation at all times, adapting to the needs of the hospital.
- Sustainability and Energy Rating: Thanks to these innovations, the project has enabled the hospital’s buildings to be energy-qualified, reducing its carbon footprint and bringing its operations into line with the most advanced sustainability standards.
In addition, the use of highly durable materials and the optimisation of the infrastructure ensure a long service life and low maintenance of the facilities.
In short, the Savener project not only improves the HUVR’s operational efficiency but also reinforces its commitment to sustainability, marking a significant step forward in the responsible management of resources and the reduction of environmental impact.